Right Fronto-Parietal
history
History
- 30 years old male with trauma
findings
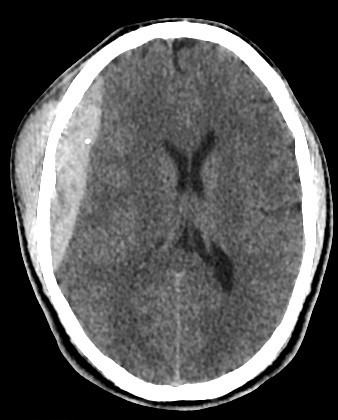
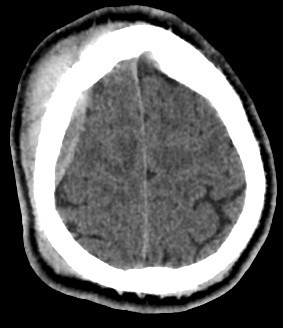
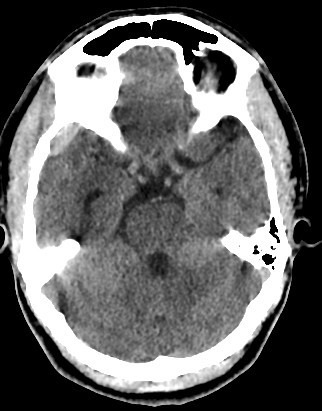
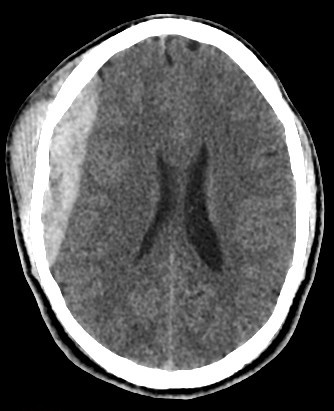
- A well-defined extraxial elliptical shape fresh blood density seen in the right fronto-parietal region.
- The lesion measured ……. cm in its maximal dimensions.
- The lesion exert little mass effect in the form of effacement of the cortical sulci and and mild midline shift.
- right fronto parietal subglial hematoma seen
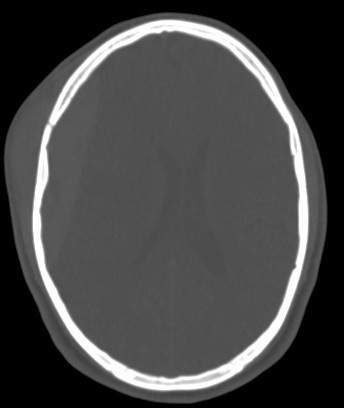
- associated right fronto parital fracture seen
- no brain herniation.
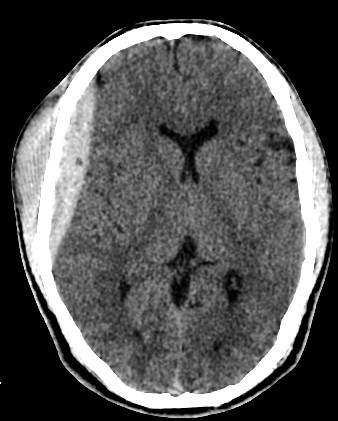
- Normal size and configuration of the ventricular system.
- No intracerebral or intraventricular recent blood density.
- Normal appearance of the brain stem and cerebellum.
diagnosis
acute extradural hematoma with fracture
explanation
CT Findings:
- Biconvex (lentiform) hyperdense collection adjacent to the inner table of the skull.
- Does not cross sutures (limited by dural attachments).
- May cross the midline if located over the falx cerebri.
- Underlying skull fracture commonly visible, especially in the temporal region.
- Mass effect: midline shift, compression of adjacent sulci or ventricles.
- Lucent areas may represent active bleeding or mixed density if subacute/chronic.
MRI Findings (if done):
- Helps in dating the hemorrhage and assessing associated parenchymal injury.
- Signal intensity varies with blood age.
- Lentiform extra-axial collection with dural attachment but no extension across sutures.
Key Differential Diagnoses:
- Subdural hematoma: Crescentic shape, crosses sutures, follows the contour of the brain.
- Hemorrhagic contusion: Intra-axial and irregular.
- Epidural abscess: Similar location but rim-enhancing on post-contrast scan.
Complications:
- Brain herniation (especially uncal).
- Midline shift and raised intracranial pressure.
- Delayed neurological deterioration (lucid interval).
Reporting Tips:
Include:
- Location and side.
- Maximum thickness and volume if possible.
- Degree of mass effect or midline shift.
- Associated fractures or pneumocephalus.
- Any additional intracranial injuries.