CT scan images of the coronary arteries with dye Forward Integration Agent
history
CT scan images of the coronary arteries HISTORY
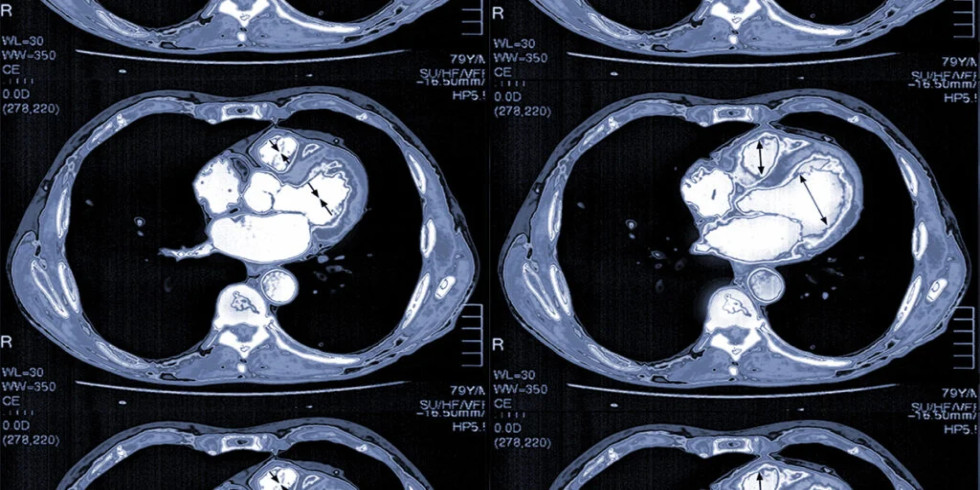
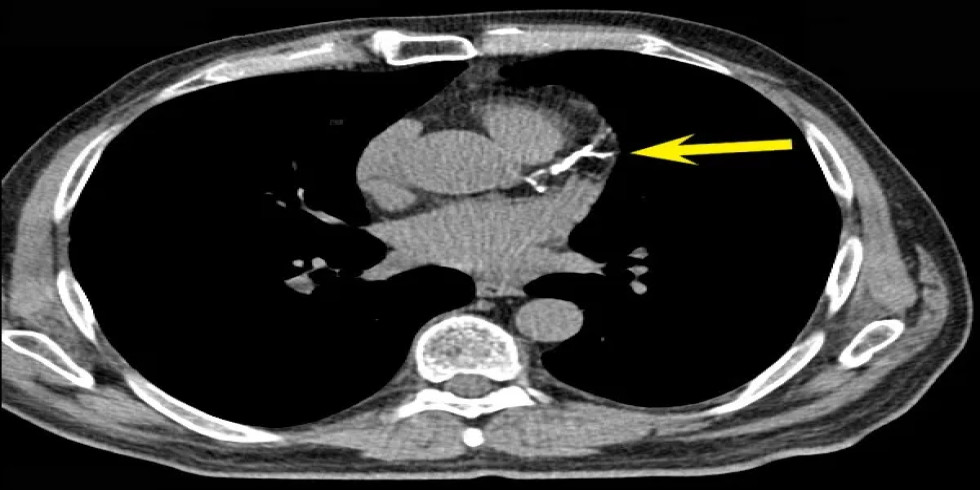
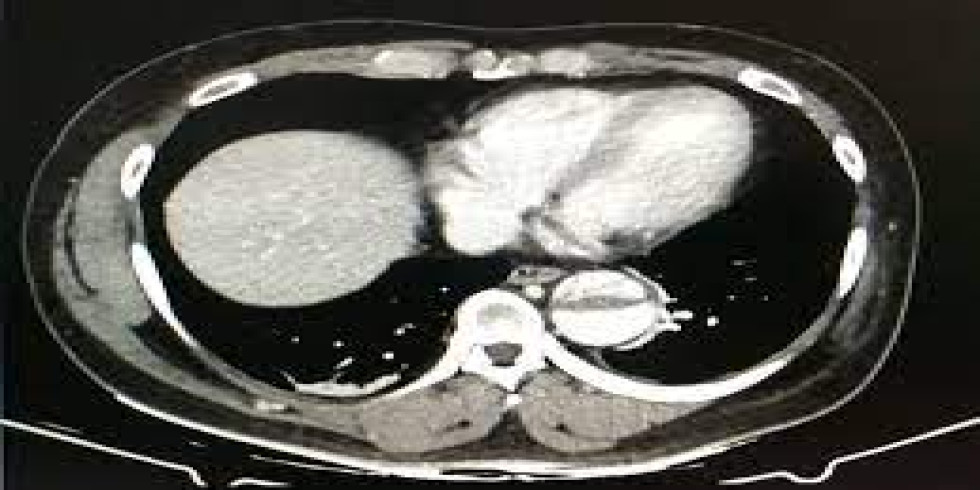
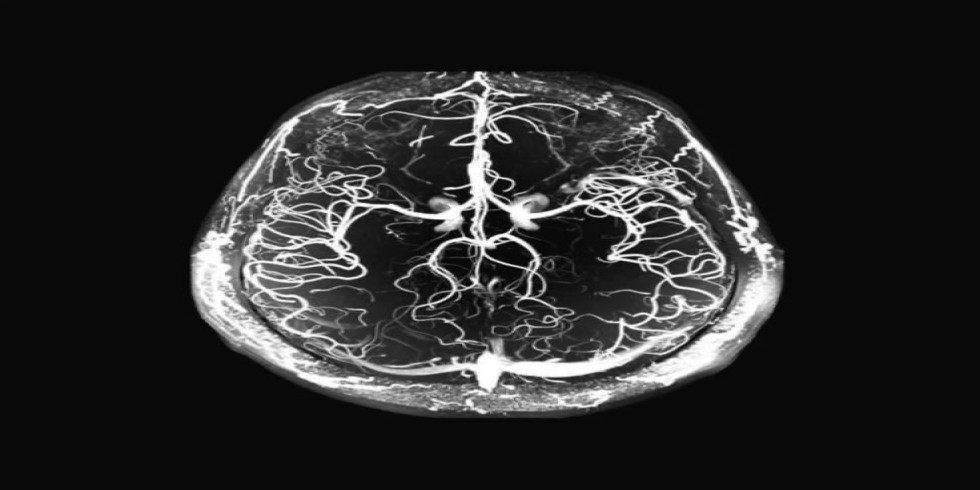
A CT coronary angiogram, also known as CTCA, is a non-invasive imaging test that uses X-rays and a contrast dye to visualize the coronary arteries and detect blockages or other abnormalities. It helps diagnose coronary artery disease by highlighting the arteries and any potential issues within them. Here's a more detailed explanation: What it is: CTCA uses a CT scanner and a contrast dye (usually iodine-based) injected into a vein, typically in the arm, to visualize the coronary arteries. The contrast dye highlights the arteries, making them appear bright on the images produced by the CT scanner, allowing doctors to see the blood flow and identify any blockages or narrowing. How it works: 1. Preparation: Patients may need to avoid eating and drinking for a certain period before the scan and may be given medication to slow their heart rate for clearer images. 2. IV Insertion: An intravenous line (IV) is inserted into a vein, usually in the arm, to administer the contrast dye. 3. Scanning: The patient lies on a table that moves into the CT scanner (a doughnut-shaped machine). The scanner rotates around the patient, taking multiple X-ray images. 4. Image Acquisition: The contrast dye highlights the coronary arteries, allowing doctors to evaluate their structure and identify any blockages, plaque buildup, or other abnormalities. 5. Post-Procedure: Patients can usually resume normal activities immediately after the scan, but may be advised to drink plenty of fluids to help flush out the contrast dye. Purpose: Detect Blockages: CTCA is used to identify blockages or narrowing (stenosis) of the coronary arteries, which can be a sign of coronary artery disease. Assess Plaque Buildup: It can detect the presence and extent of plaque buildup (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, which can restrict blood flow. Evaluate Heart Disease Risk: CTCA helps assess the overall risk of heart disease and can guide treatment decisions. Guide Further Procedures: If significant blockages are found, CTCA can help determine if further procedures like angioplasty or bypass surgery are needed. Potential Risks: Allergic Reaction: A small percentage of patients may experience an allergic reaction to the contrast dye, ranging from mild (itching, hives) to severe (difficulty breathing, anaphylaxis). Kidney Problems: In rare cases, contrast dye can potentially harm the kidneys, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney conditions. Radiation Exposure: CTCA involves exposure to X-ray radiation, but the dose is generally considered low and safe for most patients.